
#Yarn run dev server code#
Left unmanaged, code bloat can cause significant performance issues in production. The Problemįirst, unnecessary bloat: libraries, such as Vue and React, have built-in debugging tools that are essential for development but add extraneous code to a live application. development, test and production with only the code and data specifically needed for each. Webpack makes it easy to deploy multiple environments i.e. One feature I really like is the ability to easily configure separate builds based on environment variables. It’s a powerful javascript bundler that compiles all of your assets into small, production ready files.
#Yarn run dev server install#
yarn install -link-duplicatesĬreate hardlinks to the repeated modules in node_modules.If you’ve done any javascript application development recently, you’ve probably come across Webpack. Prevent yarn from creating symlinks for any binaries the package might contain.
#Yarn run dev server update#
(This may change in a later update as the feature is proven to be stable.) yarn install -no-bin-links Unlike npm, which automatically runs an audit on every install, yarn will only do so when requested. Use the yarn audit command for additional details. A count of found issues will be added to the output. yarn install -auditĬhecks for known security issues with the installed packages. Update checksums in the yarn.lock lockfile if there’s a mismatch between them and their package’s checksum. yarn install -non-interactiveĭisable interactive prompts, like when there’s an invalid version of a dependency. yarn install -ignore-optionalĭon’t install optional dependencies. Run yarn install without printing installation log. yarn install -frozen-lockfileĭon’t generate a yarn.lock lockfile and fail if an update is needed. Can not be run in a non-workspaces project or at the root of a workspaces project. Must be run inside an individual workspace in a workspaces project.

This allows you to run that workspace without building the other workspaces it depends on. Shallowly installs a package’s sibling workspace dependencies underneath its node_modules folder. yarn install -pure-lockfileĭon’t generate a yarn.lock lockfile. Notes: -production is the same as -production=true. Use this flag to instruct Yarn to ignore NODE_ENV and take its production-or-not status from this flag instead. Yarn will not install any package listed in devDependencies if the NODE_ENV environment variable is set to production. yarn install -no-lockfileĭon’t read or generate a yarn.lock lockfile. Specifies an alternate location for the node_modules directory, instead of the default. yarn install -ignore-scriptsĭo not execute any scripts defined in the project package.json and its dependencies. To investigate network performance, and can be analyzed with tools such as Network requests performed during the installation. This refetches all packages, even ones that were previously installed. These will be added to your package.json under a On the first run this will prompt you toĬhoose a single version for each package that is depended on at multiple Install all the dependencies, but only allow one version for each package. Verifies that already installed files in node_modules did not get removed. If you want to ensure yarn.lock is not updated, use -frozen-lockfile.

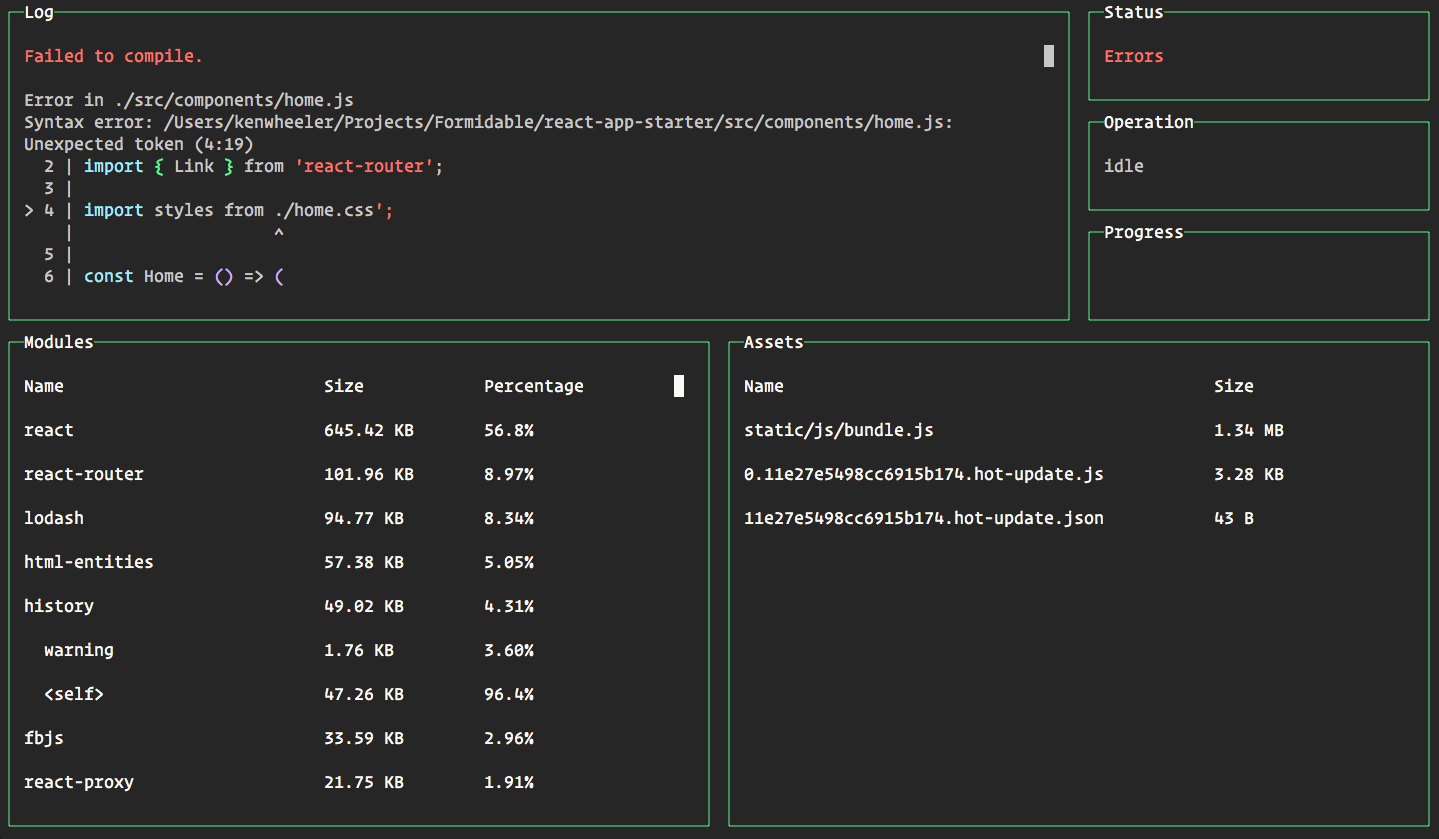
These have been replaced by yarn add and yarn add -dev. If you are used to using npm you might be expecting to use -save or This is mostĬommonly used when you have just checked out code for a project, or whenĪnother developer on the project has added a new dependency that you need to Yarn install is used to install all dependencies for a project.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
